The Ultimate Guide to the Types of USB Cables

2025-08-08 18:00
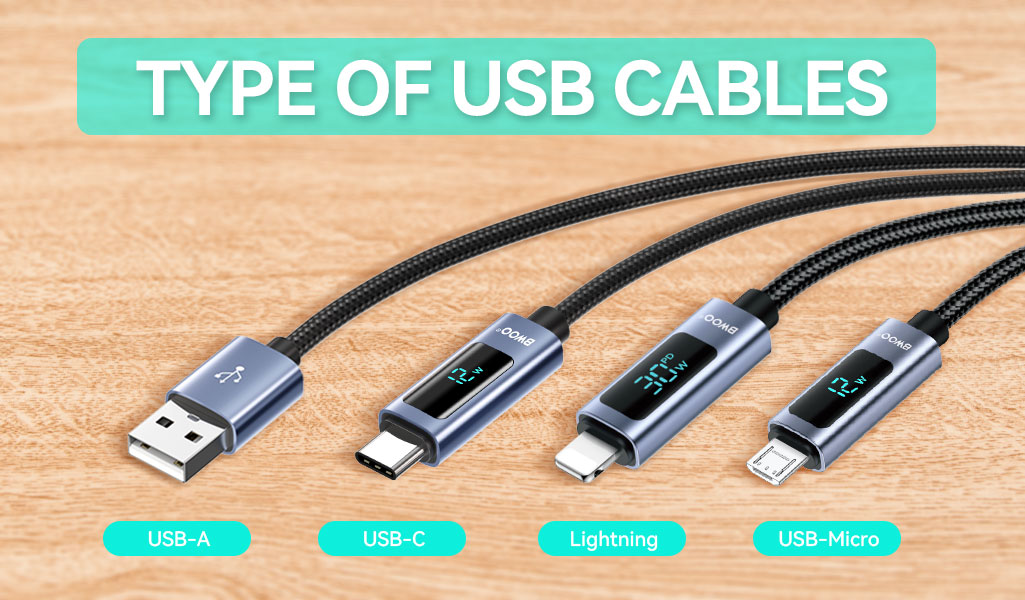
In our hyper-connected digital age, our smartphones, tablets, laptops, cameras, and countless other gadgets are indispensable extensions of ourselves. But these powerful devices share a fundamental, often overlooked dependency: the humble USB cable. It's the silent workhorse responsible for delivering power to keep us running, transferring critical data between devices, and connecting peripherals that expand functionality. Choosing the right USB cable, however, can be surprisingly complex. This guide cuts through the confusion, explaining the different types of USB connectors and the variations in USB standards.
Type of USB Cables: Connectors
The most immediate way to categorize USB cables is by their connectors. Getting the right shape is essential for a physical fit. Here are the most common types you'll encounter today:
USB Type-A (USB-A):
The classic, rectangular connector everyone recognizes. Found on computers, chargers, power banks, and older peripherals.
Primarily used on the host (power source) end of cables (e.g., plugging into a wall charger or laptop).
USB Type-B (USB-B):
A squarer connector, often with beveled corners. Less common on modern portable devices.
Traditionally used for printers, scanners, and some external hard drives. Largely being phased out in favor of USB-C.
USB Micro-B:
A small, trapezoidal connector. Was the de facto standard for Android smartphones, basic power banks, and many peripherals for years.
Charging and data transfer for older smartphones, Bluetooth speakers, controllers, etc. Note: Distinguish this from the wider Micro-USB 3.0 connector (less common).
USB Type-C (USB-C):
The modern, slim, oval-shaped connector with a reversible design (no "right side up").
The current and future standard. Found on new smartphones (iPhone 15+, Android flagships), tablets, laptops, monitors, headphones, and high-speed peripherals. Supports charging, high-speed data transfer, and video output (Display Port/HDMI Alt Modes).
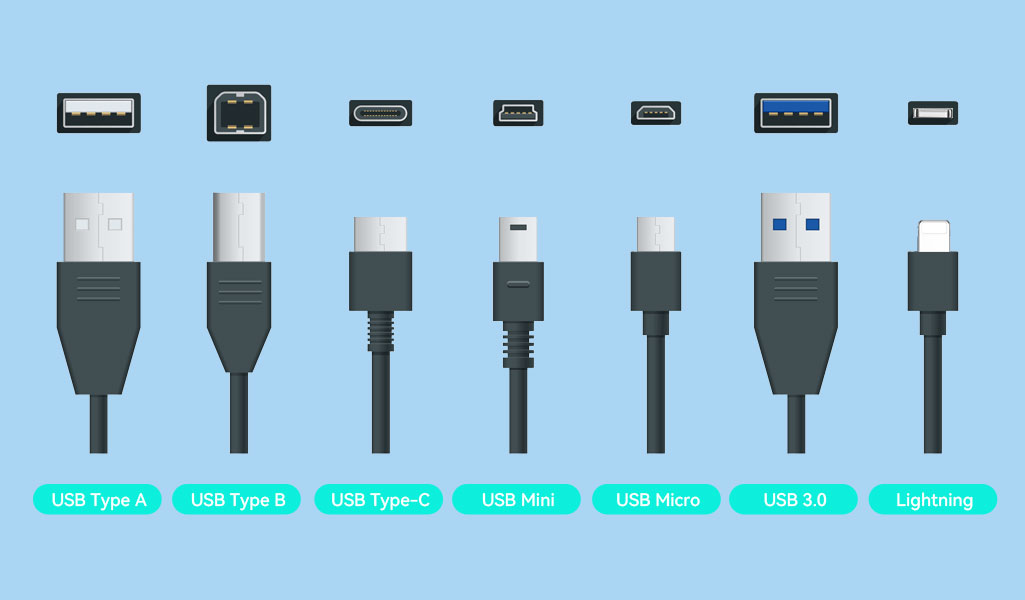

Type of USB Cables: Versions
Beyond the physical connector, the USB standard version (e.g., USB 2.0, USB 3.2, USB4) defines the cable's underlying capabilities for data transfer speed and power delivery. Crucially, the version is independent of the connector type (though USB-C enables the highest versions).
USB 2.0:
Speed: Up to 480 Mbps (Megabits per second). Suitable for basic charging and slow data transfer (keyboards, mice, older phones).
Power: Limited power delivery (typically up to 2.5W @ 5V/0.5A, sometimes higher for charging but not standardized fast charging).
Common Cables: Often uses USB-A or Micro-B connectors. Still prevalent but becoming legacy.
USB 3.2 Gen 1 (formerly USB 3.0 / USB 3.1 Gen 1):
Speed: Up to 5 Gbps (Gigabits per second). A significant jump from USB 2.0.
Power: Can support higher power delivery profiles (like USB BC 1.2) for faster charging than basic USB 2.0.
Visual ID: USB-A connectors are often blue inside. USB-C cables inherently support it. Micro-B cables have an extra "hump".
USB 3.2 Gen 2 (formerly USB 3.1 Gen 2):
Speed: Up to 10 Gbps. Ideal for fast external SSDs and high-resolution data transfer.
Power: Supports USB Power Delivery (USB PD) for significantly faster charging (commonly up to 60W, higher possible).
Common Cables: Primarily uses USB-C connectors.
USB 3.2 Gen 2x2:
Speed: Up to 20 Gbps. Requires specific USB-C cables and ports.
Power: Supports high-wattage USB PD.
USB4:
Speed: Starts at 20 Gbps (USB4 20Gbps) and goes up to 40 Gbps (USB4 40Gbps). Incorporates Thunderbolt 3/4 protocols.
Power: Supports USB PD up to 100W+.
Features: Can handle data, high-resolution video (e.g., dual 4K displays), and power simultaneously over a single USB-C cable.
USB4 Version 2.0:
The latest standard, doubling potential speeds to 80 Gbps and 120 Gbps in asymmetric mode. Requires new certified cables.
What Are the Differences Between USB Versions?
Here is a detailed comparison of types of USB cable versions.
| USB Version | Full Name | Speed(Max) | Power Delivery(Max) | Features | Common Connector |
| USB 2.0 | High-Speed USB | 480 Mbps | ~2.5W (5V/0.5A) | Basic charging & data. Legacy. | USB-A, Micro-B |
| USB 3.2 Gen1 | USB 3.0, USB 3.1 Gen 1, SuperSpeed USB 5Gbps | 5 Gbps | Up to 4.5W (5V/0.9A) or | Significant speed jump over USB 2.0. | USB-A (often blue), USB-C, Micro-B (w/ extra pins) |
| USB 3.2 Gen2 | USB 3.1 Gen 2, SuperSpeed USB 10Gbps | 10 Gbps | Supports USB PD | Fast external storage speeds. Enables PD fast charging. | Primarily USB-C |
| USB 4 | USB4 20Gbps | 20 Gbps | Up to 100W+ (USB PD) | Unified standard. Mandates USB-C. Supports data, video (DP/HDMI alt mode), & power. | USB-C (certified) |
| USB 4 2.0 | USB4 40Gbps | 40 Gbps | Up to 100W+ (USB PD) | Incorporates Thunderbolt 3. High-res video (e.g., dual 4K). | USB-C (certified, active cables often needed >0.8m) |
FAQs About Types of USB Cables
Q: Can I use a newer USB cable with an older device (or vice versa)?
A: Yes, physically compatible cables will usually work, but with limitations. Plugging a USB-C cable (supporting USB 3.2) into an older USB 2.0 port will work, but speeds and power will be limited to USB 2.0 levels. This is backward compatibility. Using an older cable (e.g., USB 2.0) with a newer device might work for slow charging or basic data but won't deliver the device's full potential speed or fast charging.
Q: What exactly is "Backward Compatibility"?
A: It means that newer versions of the USB standard are designed to work with older versions. A USB 3.2 port can accept and function with a USB 2.0 device/cable, but the connection will operate at the older, slower USB 2.0 speed and power limits.
Q: How can I tell if a USB cable supports fast charging?
A: Look for specifications:
USB Power Delivery (USB PD): This is the modern, standardized fast charging protocol for USB-C. Check the cable specs for supported PD wattages (e.g., 30W, 65W, 100W).
Legacy Protocols: For older USB-A cables, look for mentions of Qualcomm Quick Charge (QC) versions (e.g., QC 3.0, QC4+) or similar vendor-specific protocols. However, USB PD via USB-C is the universal future.
Cable Thickness: High-power cables (especially USB PD 60W+) are often thicker due to larger internal wires needed to handle the current safely. Don't rely solely on this, check specs!
Certification Marks: Look for USB-IF certification logos (e.g., USB PD logo) on packaging or product listings.
Q: Why does my high-speed USB 3.2 cable seem thicker than my old USB 2.0 cable?
A: Higher data speeds and power delivery require more internal wires and better shielding to prevent interference and ensure signal integrity and safety. Thicker gauge wires are needed to handle higher currents without overheating.
Q: How long can a USB cable be before performance suffers?
A: For basic USB 2.0 charging/data, cables can be longer (3m+). However, for high-speed data (USB 3.2 Gen 1/2, USB4) or high-power delivery (USB PD over ~60W), cable length significantly impacts performance. Generally:
USB 3.2 Gen 1/2: Best under 1 meter for full speed; up to 2-3m possible but speed may drop.
USB4 20Gbps/40Gbps & High-Power PD (100W+): Often limited to 0.8m or 1m for certified full performance. Longer cables (2m+) will typically reduce speed and/or power. Always check the cable specifications for its rated length at its maximum speed/power.
Q: Are all USB-C cables the same?
A: Absolutely not! This is critical. A USB-C cable can range from a basic USB 2.0 cable (480 Mbps, slow charging) all the way up to a certified USB4 40Gbps/Thunderbolt 4 cable supporting 40 Gbps data, 100W+ charging, and video output. Always check the supported USB version (USB 3.2 Gen 2, USB4), data speed, power delivery rating (e.g., 60W, 100W), and any features (video support) before purchasing.
Conclusion: Choose Wisely, Connect Confidently
Understanding the difference between USB connector types (A, B, Micro-B, C) and USB versions/standards (2.0, 3.2, USB4) is key to unlocking the best performance from your devices. While the move towards universal USB-C simplifies the physical connection, paying attention to the underlying capabilities (speed, power, features) remains essential.
When selecting your next cable, especially for fast charging your smartphone or transferring large files quickly, prioritize cables that clearly state their specifications – look for USB Power Delivery (PD) ratings and USB version/speed (like USB 3.2 Gen 2 or USB4).
Related readings:
How to Choose a Good Data Cable?
Comment
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required. Required fields are marked*














































Comment
There are no comments yet!