What is PD Fast Charging?

2023-11-01 09:27
With the popularity of Type-C interfaces in devices, PD fast charging has become one of the most prevalent fast-charging protocols for USB-powered devices. With impressive charging efficiency and safety performance, it allows us to charge our devices with less charging time than standard USB chargers However, what PD fast charging is may not be clear to us. Today, we will share a detailed introduction to it with you.

What is PD fast charging?
PD fast charging, referred to as the USB Power Delivery Specification, is a charging standard debuted by the USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum). This power delivery specification challenges the original charging standard, like Quick Charge QC charging standard, and achieves an unprecedentedly faster and more efficient charging speed.
PD fast charging is a universal charging standard that can be used on a wide range of devices to achieve fast charging.Based on a USB-C connector, it delivers more powerful charging capabilities. For example, it redefines how devices can supply electricity over the USB-C port and how these devices are identified and handled. Besides, it also enhances the power level of the Type-C port from 5V/2A to 20V/5A (100W), which enables it to work with power-hungry devices, including monitors and laptops. With more upgrades made to this charging specification in recent years, the latest version has been launched to support 240 watts of power.
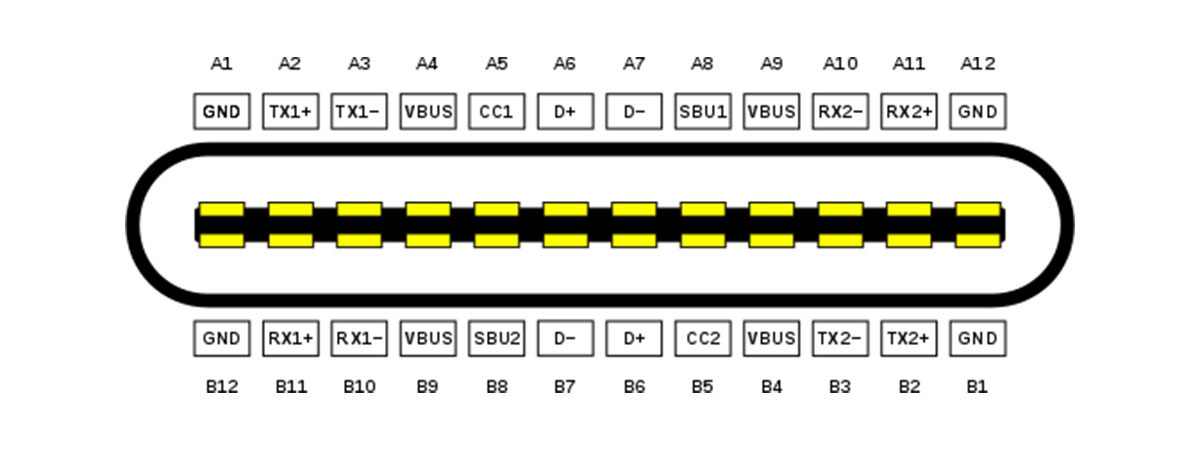
The Features of USB Power Delivery
USB Power Delivery introduces a completely new power delivery method for USB gadgets. With its unique features, it distinguishes itself from multiple private charging protocols.
● More Powerful Power Delivery Capability
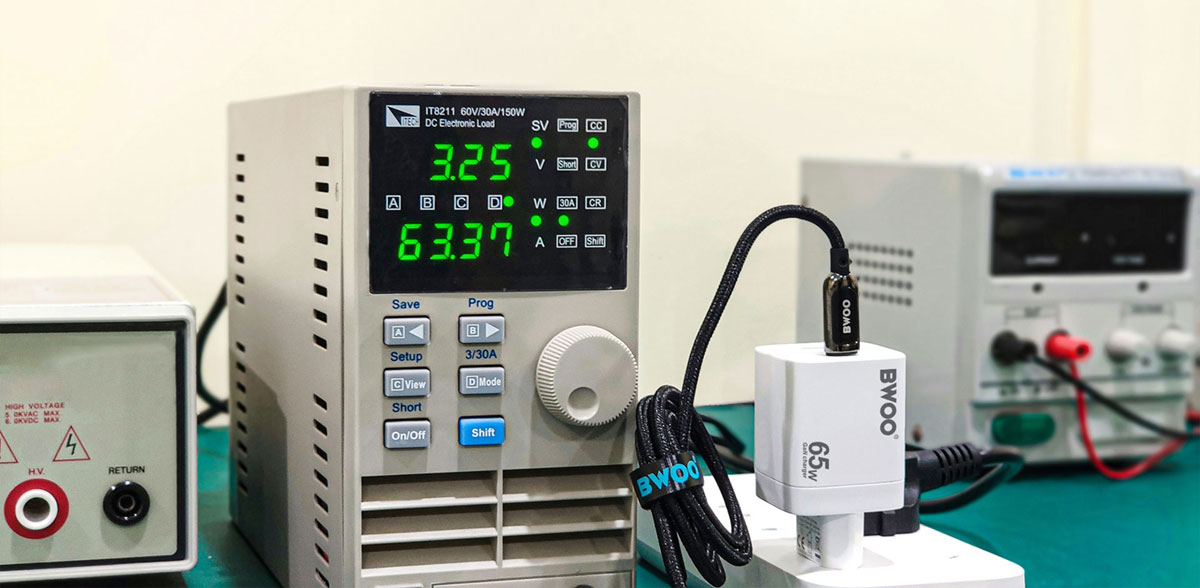
USB PD standard offers powerful power delivery capabilities. Traditional USB cables allow only 2.5W, while USB type-C cables can offer 15W (5V/3A) and even carry 5A current at 20V to deliver a maximum power of 100W using the USB PD power. The PD 3.1 specification supports a maximum power of 240W, making it universal for both low-power devices and power-hungry electronics like laptops and power stations.

● Role Swap
USB PD3.0 supports fast role swapping (FRS) capability, allowing a device to make a role switch between source and sink, which greatly enhances the efficiency of USB. To enable role swap, a device must come with a dual-role power port (DRP). Based on the DRP port, the device can work as a sink or source. For example, if a laptop can consume power and, through the DRP port, receive power, then it is a sink. Thanks to role swap, the laptop can transform into the source to charge your phone, and this change can be implemented within 150μs without having to reconnect the cable.
Essentially, BWOO P51 dual-way fast-charging power banks are based on role swapping. It has a DRP port through which it can feed power to your device—the power bank is the source. And the power bank can receive power to recharge itself—the power bank is the sink. This process is also what we call the bi-directional charging feature of a power bank.

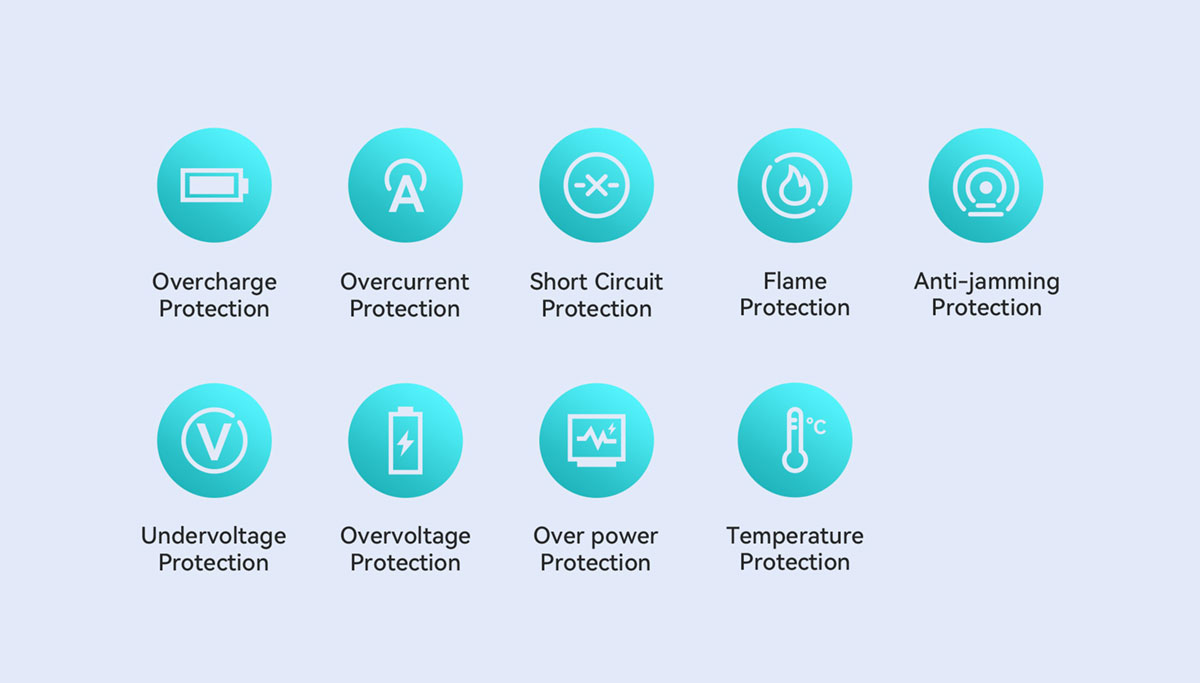
● Protection Circuit
Hazards about voltage, current, and temperature seem to coexist with electronic devices. That is the reason why many people have doubts about PD's fast charging.
However, is it safe to use USB PD fast charging technology? Absolutely yes, it is. This is because this charging protocol supports a comprehensive detection of problems with voltage, current, and temperature, which protects your devices from damage and helps to adjust the system on time before there are any potential risks.
According to the PD3.1 version specification, this version enables power supply reduction to deal with possible risks such as overvoltage, overcurrent, overtemperature, and more.
Meanwhile, it provides a safer and more intelligent charging solution. For example, chargers, data cables, and power banks from BWOO that include a PD fast charging chip can recognize the connected device and the power required to charge it as quickly as possible. This negotiation ensures fast charging without delivering too much power or damaging the device's circuitry.
Different versions of USB PD
Since its launch, USB power delivery has evolved a lot and generated different versions to benefit us in device charging. Here we will reveal how it evolves.

● PD1.0
USB PD1.0 is the basic version, but it works more amazingly than QC1.0 of the same period. Unlike QC1.0, which supports a fixed power of only 5V/2A for all the devices, it recommends six power profiles for different types of USB power devices, including 10W (5V2A), 18W (12V1.5A), 36W (12V3A), 60W (12V5A), 60W (20V3A), and 100W(20V5A). However, this version is not favored by a wide range of gadgets, even low-voltage smartphones, because Type-A and Type-B were still the mainstream ports for USB power devices at that time.
● PD2.0
In August 2014, USB-IF released PD2.0 to us. This power delivery specification supports more current and voltage modes, including 5V3A, 9V3A, 12V3A, 15V3A, and 20V5A, and enables a maximum output of 100W. Besides, it stipulates that the Type-C port is the standard interface for the PD protocol and announces more capabilities of Type-C, such as charging, data transfer, audio transmission, and video transmission, as well as compatibility with Thunderbolt protocols.
However, it was not popular at the early launch of PD2.0. Till 2015, when Apple used the USB PD2.0 protocol in its new MacBook, the Type-C port and USB PD caught on among electronic gadgets, and the competition for the mainstream interface between Type-A and Type-C started with it.
● PD3.0
USB PD3.0 was launched in November 2015. Based on PD2.0, this standard introduces a more detailed description for the built-in battery of the device, such as a digital certificate and digital signature functions, and supports device hardware and software version authentication for safe inter-device operation while allowing for software updates through PD communication. In addition, another extension introduced by USB Power Delivery 3.0 is fast role swap, which enables devices to switch roles as power providers and power consumers.
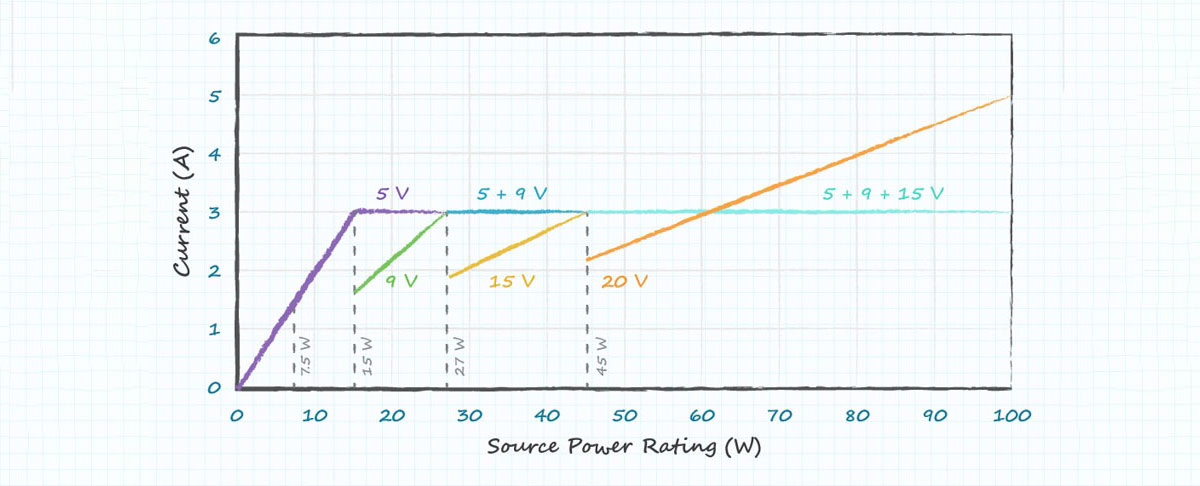
In February 2017, USB PD3.0 made a vital update by introducing the Programmable Power Supply (PPS). This power rule integrates the two current charging modes: high voltages with low current and low voltages with high current, allowing for configurable voltage granular increments at 20 mV, which is only one-tenth of that of QC3.0. Meanwhile, PPS provides a more flexible and efficient charging method by making stepwise changes in voltage and current to present a more optimal voltage pattern for less heat and energy loss while charging.
● PD3.1
2021 witnessed the release of PD3.1 power delivery specifications. This version has many valuable updates. It successfully breaks the power limits of 100W of PD2.0 and PD3.0 and enhances PD charging power to 140W, 180W, and a maximum of 240W by offering more configurable voltage modes, including 28V, 36V, and 48V. Besides, it allows for smaller voltage granular increments of 10mV. And the result is more efficient charging and a wider application in a handful of electronics, including not only low-voltage devices like smartphones and earphones but also high-power devices such as gaming laptops, electric bicycles, and televisions.
Is a PD charger the same as USB-C?
When it comes to USB-C, many people take it for granted that all the devices with a USB-C port can support the USB PD fast charging standard, and they even mistakenly believe that PD chargers are the same as USB-C.
USB-C and USB-PD are totally different things. The key difference between them is that the former is a new interface specification, while the latter is a fast-charging protocol.

USB-C, the abbreviation of USB Type-C ( commonly called Type-C ), is a universal serial bus for all USB devices. It is a 24-pin connector with rotational synchronization, which allows you to use it in either orientation, bringing a more convenient user experience. That is why many devices give up the Micro-USB port and head to the Type-C ports. However, not all USB-C devices support the USB-PD fast charging standard. If you do not know clearly whether your USB-C device supports USB-PD standards, you can check it on the charger or consult the supplier you bought it from.
Furthermore, there is no denying the fact that it is the USB PD that maximizes the power of this kind of interface. At the very beginning, a Type-C port supports a maximum power of 5V/3A, while it can support a maximum output of 240W using the USB-PD fast charging protocol.
However, is USB-PD only used in USB-C? The answer is no. According to the Power Delivery Specification Revision 1.0, USB-PD can work through Type-A and Type-B ports. However, due to the limitations of USB-A, a Type-C to USB-A cable can not charge as fast as a USB-C to USB-C cable. That is also why 100W fast charging cables are available and many smartphones offer a USB-C cable.
The Future of USB Power Delivery
USB PD was created as a standard power rule to power a wide range of USB gadgets, with the aim of reducing the need for proprietary ports, connectors, and plugs. In the past ten years, USB PD has made a series of valuable updates. Currently, PD fast charging, using a USB-C port, not only enables charging power from 15W to 240W to meet the changing needs of most electronic devices but also allows for more impressive functions, including quick data transfer, high-speed video and audio transmission, etc. That is why many suppliers have given up micro-USB and switched to the Type-C interface. Now it has become popular in consumer electronics, including mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and monitors.

Apple, the first to recommend the PD protocol in the Macbook in 2015, has attached a Type-C to Lightning cable to its iPhone 12 series. According to reliable sources, the upcoming iPhone 15 series will use a Type-C port. Therefore, it is predicted that USB Power Delivery will become a unified charging technology in the future. It is worth noting that the unification of USB PD may bring E-waste to the earth due to the discarded old chargers and cables, but all this effort is to avoid more E-waste in the future.
BWOO, with 20 years of dedication and precipitation in consumer electronics, has kept a deep insight into the development and trends within this industry while engaging in providing unparalleled, valuable electronics for people across the globe.
Our R&D team adopts high-end PD fast charging chips, combining with the most feasible product design schemes, to create a series of industry-leading PD fast charging-enabled products, including chargers, data cables, and power banks. Whether you are looking for PD3.1 chargers and data cables, or dual-way fast-charging power banks, you can get the best one.
BWOO Products that support PD fast charging
 |  |  |
Comment
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required. Required fields are marked*












































Comment
There are no comments yet!